- Home
- Balanced Corpus of Contemporary Written Japanese
- Integration of Morphological Information in XML (M-XML)
Integration of Morphological Information in XML (M-XML)
M-XML is an implementation based off the C-XML format which gives information on the linguistic structure of both Fixed and Variable Length Samples - it allows for the embedding of morphological and syntactic information concerning both Long and Short Unit Words, and allows easy access to such linguistic data. M-XML contains the following layers of information concerning lexical items:
Layered Structure of Morphological Information in XML Format
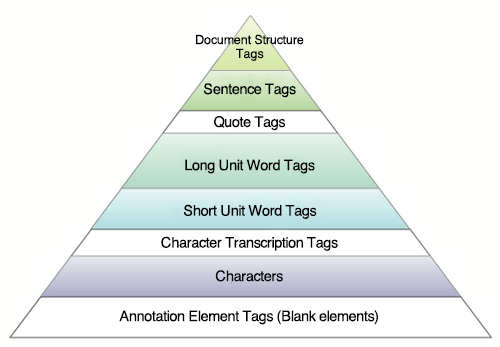
Differences from C-XML
The primary differences between C-XML and M-XML are outlined in the following sections.
1. Integration of Sentence Structure Information for Variable Length Samples
M-XML retains only sentence structure information for Variable Length Samples, and fixed length portions selected from Variable Length Samples are surrounded by simple containers. Only inline elements are retained.
2. Unification of Sentence Definitions
Due to some variable sentence definitions used in C-XML for samples of sources such as online knowledge bases, blogs, textbooks, and poetry being merged with sentence definitions in M-XML, certain tags particular to different sub-corpora were changed.
3. Revisions to Sentence Tags
C-XML allows for the recursive nesting of sentence tags, but this was revised in M-XML. In M-XML, a top-level sentence tag changes to the SuperSentence tag, while any a subordinate sentence remains the same. Text following a superSentence tag will be marked with the new notation of sentence type="Fragment".
4. Revisions to Nested Tags
In cases where the ruby or quote tages conflict with or obscure tags giving morphological information, they will be amended.
5. Supplement to the NumTrans Tag
In portions where calculations would be transformed into representative numbers, the NumTrans and fraction tags have been appended.
Example of the Structuring of Morphological Information
Below is an example of M-XML markup on a single extracted sample of a sentence element. For ease of viewing some properties have been omitted.
<LUW B="B" SL="v" l_lemma="公共工事請け負い金額" l_lForm="コウキョウコウジウケオイキンガク" l_wType="混" l_pos="名詞-普通名詞-一般" >
<SUW lemma="公共" lForm="コウキョウ" wType="漢" pos="名詞-普通名詞-一般" pron="コーキョー">
公共
</SUW>
<SUW lemma="工事" lForm="コウジ" wType="漢" pos="名詞-普通名詞-サ変可能" pron="コージ">
工事
</SUW>
<SUW lemma="請け負い" lForm="ウケオイ" wType="和" pos="名詞-普通名詞-一般" pron="ウケオイ">
請負
</SUW>
<SUW lemma="金額" lForm="キンガク" wType="漢" pos="名詞-普通名詞-一般" pron="キンガク">
金額
</SUW>
</LUW>
<LUW SL="v" l_lemma="の" l_lForm="ノ" l_wType="和" l_pos="助詞-格助詞" >
<SUW lemma="の" lForm="ノ" wType="和" pos="助詞-格助詞" pron="ノ">の</SUW>
</LUW>
<LUW B="B" SL="v" l_lemma="動き" l_lForm="ウゴキ" l_wType="和" l_pos="名詞-普通名詞-一般" >
<SUW lemma="動き" lForm="ウゴキ" wType="和" pos="名詞-普通名詞-一般" pron="ウゴキ">
動き
</SUW>
</LUW>
(略)
</sentence>